Key Features
KubeSlice makes Kubernetes simple at scale for multi cluster/multi-tenant/ multi-region/multi-cloud application deployments. It is a platform that combines network, application, Kubernetes, and deployment services to bring uniformity across clusters for multi-cluster applications, thus dramatically increasing development velocity for platform and product teams.
Features Summary
The following table summarizes the key features of KubeSlice.
| Main Feature | Sub Feature | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Application Management | Namespace Sameness | Ensures namespace sameness across clusters or cloud. Allows applications to be deployed with namespace parity for simplified management and portability. |
| Service Exports and Service Imports | Automatically discovers and exposes services across cluster boundaries, enabling cross-cluster service connectivity without manual configuration. | |
| Isolation | Allows isolation by association of application namespaces with a slice. | |
| Network | East-West Cluster Communication | Establishes secure, per-slice tunnels between clusters, forming an overlay Layer 3 network for seamless communication. Supports ingress and egress gateways for East–West traffic. |
| Eliminate IP Address Conflicts | Uses a non-overlapping RFC1918 address space to remove the complexity of overlapping CNI CIDRs across cloud, data center, and edge environments. | |
| QoS Profiling | Defines Quality of Service (QoS) profiles per slice, allowing granular traffic control and prioritization for inter-cluster network traffic. | |
| Security and Governance | Multi-Cluster Multi-Tenancy Security | Provides secure isolation and encrypted connectivity between tenants across clusters, enforcing slice-level security boundaries. |
| Multi-Cluster RBAC Policies | Propagates Role-Based Access Control configurations consistently across all clusters and slices in a workspace. | |
| Resource Quotas and Policy Management | Applies and enforces CPU, memory, and storage quotas along with policies across clusters for fair resource allocation. | |
| Multi-Tenancy | Multi-Cluster, Multi-Cloud, and On-Prem Support | Enables consistent multi-tenancy across clusters spanning cloud, on-premises, and edge environments, providing unified management and isolation. |
| Application and Namespace Isolation | Segregates applications and namespaces across slices for tenant isolation and resource governance. | |
| Multi-Cluster Networking | Layer 3 (L3) Pod-to-Pod Connectivity | Provides flat, cross-cluster Layer 3 connectivity between pods using a secure overlay network. |
| Multi-Cluster Service Mesh | Integrates service mesh capabilities across clusters for consistent service discovery, routing, and observability. | |
| Overlay East–West Gateways (Envoy Gateways) | Uses Envoy-based gateways to enable east–west inter-cluster traffic routing and policy enforcement. | |
| Multi-Cluster Routes and GLB Integration | Supports Global Load Balancer (GLB) with external DNS for unified ingress and intelligent traffic routing across clusters. | |
| North–South and VPC Egress Connectivity (KubeAccess) | Enables secure north–south connectivity and overlay VPC egress gateways to access external cloud services or on-prem VM workloads. | |
| Slice Overlay Network | No-Network Overlay | Provides no overlay network, enabling cluster isolation while supporting RBAC, resource quota management, and node affinity. Switching to single/multi-network overlay is allowed only if all clusters have networking enabled; switching back is unsupported. |
| Single-Network Overlay | Creates a single, flat L3 overlay network across clusters with pod-to-pod connectivity. Service discovery is handled through slice DNS. | |
| Multi-Network Overlay | Uses ingress or egress gateways managed through Gateway API for inter-cluster connectivity at L7 (HTTP/HTTPS). No flat L3 network; service discovery uses local cluster IP services. | |
| Service Discovery | Auto Discovery of Services | Enables automatic service discovery across clusters participating in a slice, simplifying cross-cluster communication. |
| DNS Entry Management | When a service is exported within a slice, the Slice Operator creates and distributes DNS entries across all participating clusters, ensuring seamless and consistent service resolution. | |
| Application Replication | Replication Slice | Enables efficient replication of applications between clouds or data centers using a replication slice. Replicated namespaces can be managed in an application slice. |
| Backup and Restore Applications | Allows namespace backup and restore using a replication slice by specifying the same cluster as both source and destination during slice creation. | |
| KubeTally | Multi-Cluster Cost Tracking | Provides cost tracking and resource usage insights across multiple clusters. Enables chargeback visibility for resources such as Compute, PersistentVolume, and LoadBalancer. |
| Workload Management | Multi-Cluster CPU Workload Placement | Automatically distributes workloads across clusters based on CPU availability, policies, or performance needs to optimize utilization. |
| Multi-Cluster Bursting of Microservices | Enables dynamic scaling (bursting) of microservices across clusters to handle demand surges and ensure availability. |
Slice Overlay Network Deployment Mode
KubeSlice supports the following overlay network types for inter-cluster connectivity:
- No-network overlay
- Single-network (default option) overlay
- Multi-network overlay
No-network Overlay
This option is also referred to as No Connectivity. It provides no overlay network that is no inter-cluster connectivity among all clusters of a slice. The main benefit of this mode is that you can manage all your clusters on a slice and estimate their costs and isolate clusters from communicating with each other cluster on the no-network slice. This no-network slice supports the operations such as RBAC, resource quota management, and node affinity.
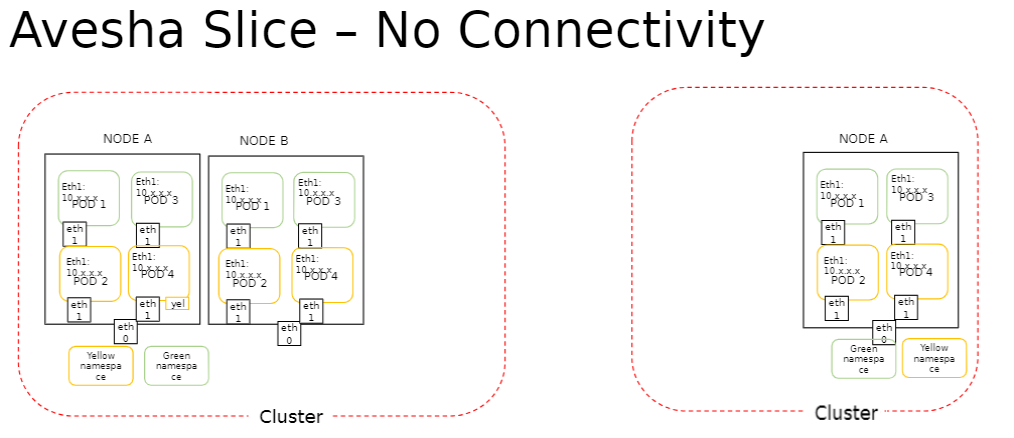
The participating clusters of a no-network overlay slice contains networking enabled to true by default. Thus this property facilitates switching a slice from no-network overlay to single or multiple network overlay slice only when all the clusters on that slice have networking enabled. However, switching back from single/multi-network overlay to no-network overlay is unsupported.
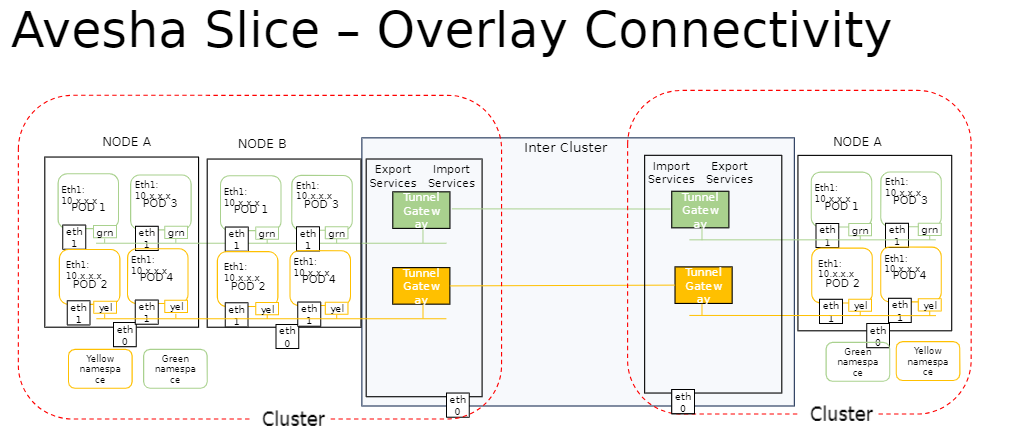
Single-Network Overlay
This option is also referred to as Overlay Connectivity. It provides a single, flat, overlay network across all the clusters of a slice. The pod-to-pod connectivity is provided at L3, with each pod receiving a unique IP address. The service discovery relies on the slice DNS to resolve service names exposed on a slice.
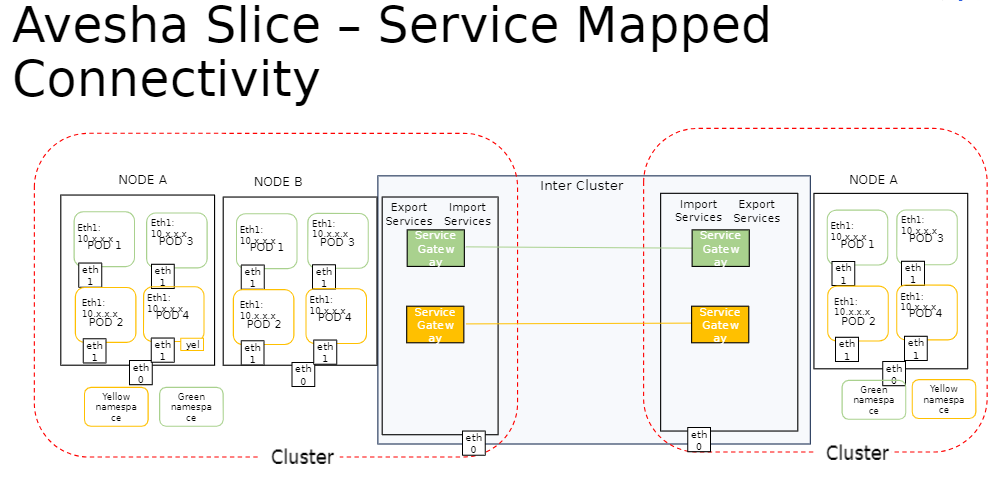
Multi-Network Overlay
This option is also referred to as Service Mapped Connectivity. It sets up the inter-cluster connectivity for applications by creating and managing a network of ingress and egress gateways based on the Gateway API. The pod-to-pod connectivity is provided at L7 for HTTP and HTTPS protocols. Unlike the single-network option, there is no flat inter-cluster network at L3. The service discovery for application services exposed on a slice is provided through local cluster IP services.
Differences Between Single-Network and Multi-Network Slice Overlay
The figure below illustrates the difference between the single-network and multi-network overlay.
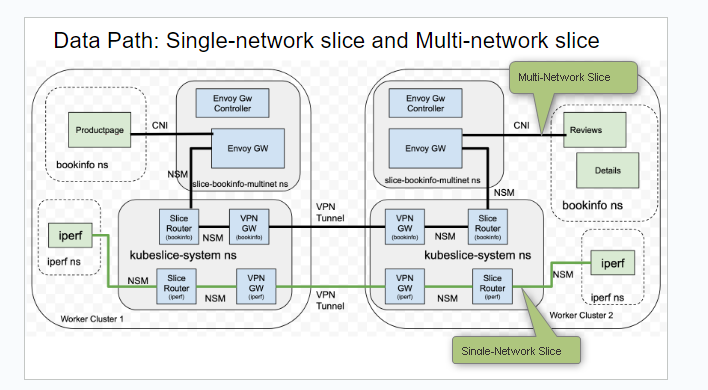
| Single-Network Slice | Multi-Network Slice |
|---|---|
| There is single flat overlay network and pod-to-pod connectivity is at L3. | The pod to pod connectivity across clusters is set up through a network of L7 ingress and egress gateways. There is no L3 reachability. |
| The application pod receives a new interface and an IP address. | The application pod is left untouched. There is no new interface injection or new IP address for the pod. |
| The application service discovery is through KubeSlice-DNS and service import/export mechanism. There is no cluster IP address. | The application service discovery is through the local cluster IP service and Kubernetes-DNS. |
| HTTP, HTTPs, TCP, and UDP are the supported protocols. | Only HTTP and HTTPs are the supported protocols. |
IP Address Management
IP Address Management (IPAM) is a method of planning, tracking, and managing the IP address space
used in a network. On the KubeSlice Manager, the Maximum Clusters parameter of the slice creation
page helps with IPAM. The corresponding YAML parameter is maxClusters.
This parameter sets the maximum number of worker clusters that you can connect to a slice. The maximum number of worker clusters affects the subnet calculation of a worker cluster. The subnet in turn determines the number of host addresses a worker cluster gets for its application pods.
For example, if the slice subnet is 10.1.0.0/16 and the maximum number of clusters is 16, then each cluster gets a subnet of 10.1.x.0/20, where x = 0, 16, or 32.
This is a significant parameter that can only be configured during slice creation. If this parameter is not set, it defaults to 16.
The subnet of a worker cluster determines the number of host addresses that are available to that cluster. Hence, you must be prudent and cautious when you set the maximum worker clusters. The value of the maximum number of clusters set remains constant for the entire life of a slice, and it is immutable after a slice is created.
The fewer the clusters, the more IP addresses are available for the application pods of every worker cluster that is part of a slice. By default, the value of the Maximum Clusters parameter is 16. The supported value range is 2 to 32 clusters.
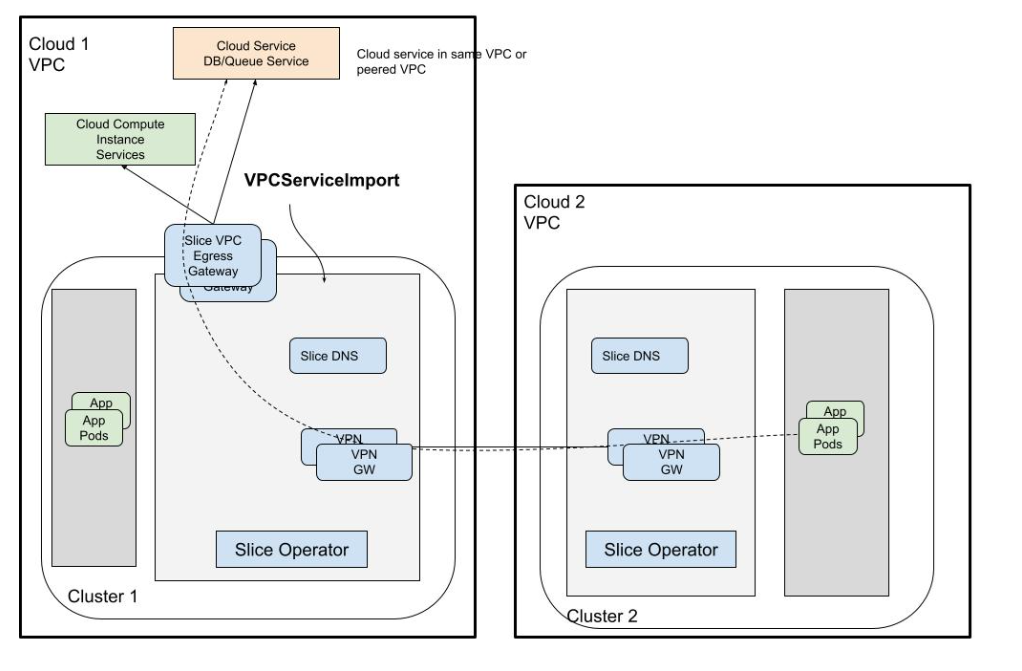
Connectivity to Clusters in Private VPCs
In addition to connecting public clusters, KubeSlice can also be used to connect clusters that are enclosed within a private VPC. Such clusters are accessed through network or application Load Balancer that are provisioned and managed by the cloud provider. KubeSlice relies on network Load Balancers to setup the inter-cluster connectivity to private clusters.
The following picture illustrates the inter-cluster connectivity set up by KubeSlice using a network Load Balancer (LB).
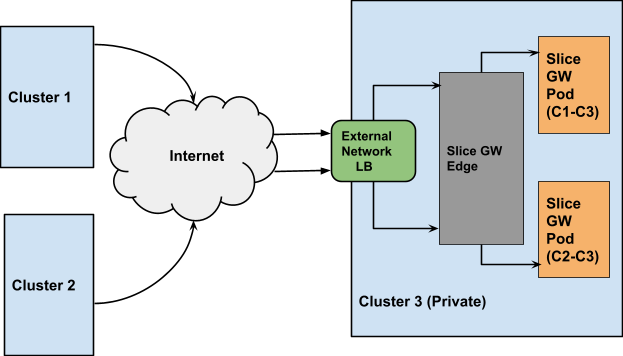
Users can specify the type of connectivity for a cluster. If the cluster is in a private VPC, the user can utilize the
LoadBalancer connectivity type to connect it to other clusters. The default value is NodePort. The user can also configure the gateway
protocol while configuring the gateway type. The value can be TCP or UDP. The default value is UDP.
Managed Services Gateway
KubeSlice provides access to private cloud managed services in a VPC through an Envoy-Proxy-based egress gateway. The VPC egress gateway feature enables users to import a private managed service running outside a Kubernetes cluster into a slice. This allows the application pods running in remote clusters to access the managed service through the slice network.
When a worker-cluster with direct access to the cloud managed service in its own VPC is connected to a slice, all the other worker-clusters that are part of the same slice can now access the managed service.
The following figure illustrates how application pods access a cloud-managed service that is onboarded onto a slice.