Clone the Repository to Install EGS Using the Script
This topic describes the steps to install EGS on the Kubernetes cluster using the script provided in the egs-installation repository. The installation process involves cloning the repository, checking prerequisites, modifying the configuration file, and running the installation script.
Clone the Repository
Clone the EGS installation repository using the following command:
git clone https://github.com/kubeslice-ent/egs-installation.git
- Ensure the YAML configuration file is properly formatted and includes all required fields.
- The installation script will terminate with an error if any critical step fails, unless explicitly configured to skip on failure.
- All file paths specified in the YAML must be relative to the base_path, unless absolute paths are provided.
Check for Prerequisites
Use the egs-preflight-check.sh script to verify the prerequisites for installing EGS.
-
Navigate to the cloned repository and change the file permission using the following command:
chmod +x egs-preflight-check.sh -
Use the following command to run the script:
./egs-preflight-check.sh --kubeconfig <ADMIN KUBECONFIG> --kubecontext-list <KUBECTX>
Create Namespaces
If your cluster enforces namespace creation policies, pre-create the namespaces required for installation before running the script. This step is optional and only necessary if your cluster has such policies in place.
You can use the create-namespaces.sh script to create the required namespaces. Use the following command to create namespaces:
./create-namespaces.sh \
--input-yaml namespace-input.yaml \
--kubeconfig ~/.kube/config \
--kubecontext-list context1,context2
You must ensure that all required annotations and labels for policy enforcement are correctly configured in the
namespace-input.yaml file.
Prerequisites for Controller and Worker Clusters
You can use the egs-install-prerequisites.sh script to configure and install prerequisites for EGS.
-
Controller cluster prerequisites: Verify EGS Controller Prerequisites for:
- Prometheus configuration
- PostgreSQL configuration
-
Worker cluster prerequisites: Verify EGS Worker Prerequisites for:
- GPU Operator installation and configuration
- Prometheus configuration and Monitoring requirements
-
Before running the prerequisites installer, you must configure the
egs-installer-config.yamlfile to enable additional applications installation:# Enable or disable specific stages of the installation
enable_install_controller: true # Enable the installation of the Kubeslice controller
enable_install_ui: true # Enable the installation of the Kubeslice UI
enable_install_worker: true # Enable the installation of Kubeslice workers
# Enable or disable the installation of additional applications (prometheus, gpu-operator, postgresql)
enable_install_additional_apps: true # Set to true to enable additional apps installation
# Enable custom applications
# Set this to true if you want to allow custom applications to be deployed.
# This is specifically useful for enabling NVIDIA driver installation on your nodes.
enable_custom_apps: false
# Command execution settings
# Set this to true to allow the execution of commands for configuring NVIDIA MIG.
# This includes modifications to the NVIDIA ClusterPolicy and applying node labels
# based on the MIG strategy defined in the YAML (e.g., single or mixed strategy).
run_commands: falsenoteimportant configuration in the
egs-installer-config.yamlfile:- Set
enable_install_additional_appstotrue: This enables the installation of GPU Operator, Prometheus, and PostgreSQL. - Set
enable_custom_appstotrue, if you need NVIDIA driver installation on your nodes. - Set
run_commandstotrue, if you need NVIDIA MIG configuration and node labeling.
- Set
-
After configuring the YAML file, run the
egs-install-prerequisites.shscript to set up GPU Operator, Prometheus, and PostgreSQL:./egs-install-prerequisites.sh --input-yaml egs-installer-config.yamlThis step installs the required infrastructure components before the main EGS installation
Modify the Configuration File
-
Navigate to the cloned
egs-installationrepository and locate the input configuration file namedegs-installer-config.yaml. -
Edit the
egs-installer-config.yamlfile with the globalkubeconfigandkubecontextparameters:global_kubeconfig: "" # Relative path to global kubeconfig file from base_path default is script directory (MANDATORY)
global_kubecontext: "" # Global kubecontext (MANDATORY)
use_global_context: true # If true, use the global kubecontext for all operations by default -
(AirGap installation only) If you are performing an AirGap installation, update the
image_pull_secretssection in the config file with appropriate registry credentials or secret references. You can skip this step if you are not performing AirGap installation.# From the email received after registration with Avesha
IMAGE_REPOSITORY="https://index.docker.io/v1/"
USERNAME="xxx"
PASSWORD="xxx" -
(Optional) These settings are required only if you are not using local Helm charts and instead pulling them from a remote Helm repository:arts)
-
Set
use_local_chartsto falseuse_local_charts: false -
Set the Global Helm repository URL
global_helm_repo_url: "https://smartscaler.nexus.aveshalabs.io/repository/kubeslice-egs-helm-ent-prod"
-
-
(Optional): You can customize the installation process by enabling or disabling specific components and additional applications. The following configuration options are available:
# Enable or disable specific stages of the installation
enable_install_controller: true # Enable the installation of the Kubeslice controller
enable_install_ui: true # Enable the installation of the Kubeslice UI
enable_install_worker: true # Enable the installation of Kubeslice workers
# Enable or disable the installation of additional applications (prometheus, gpu-operator, postgresql)
enable_install_additional_apps: false # Set to true to enable additional apps installation
# Enable custom applications
# Set this to true if you want to allow custom applications to be deployed.
# This is specifically useful for enabling NVIDIA driver installation on your nodes.
enable_custom_apps: false
# Command execution settings
# Set this to true to allow the execution of commands for configuring NVIDIA MIG.
# This includes modifications to the NVIDIA ClusterPolicy and applying node labels
# based on the MIG strategy defined in the YAML (e.g., single or mixed strategy).
run_commands: false -
Update the KubeSlice Controller (EGS Controller) configuration, in the
egs-installer-config.yamlfile:#### Kubeslice Controller Installation Settings ####
kubeslice_controller_egs:
skip_installation: false # Do not skip the installation of the controller
use_global_kubeconfig: true # Use global kubeconfig for the controller installation
specific_use_local_charts: true # Override to use local charts for the controller
kubeconfig: "" # Path to the kubeconfig file specific to the controller, if empty, uses the global kubeconfig
kubecontext: "" # Kubecontext specific to the controller; if empty, uses the global context
namespace: "kubeslice-controller" # Kubernetes namespace where the controller will be installed
release: "egs-controller" # Helm release name for the controller
chart: "kubeslice-controller-egs" # Helm chart name for the controller
#### Inline Helm Values for the Controller Chart ####
inline_values:
global:
imageRegistry: docker.io/aveshasystems # Docker registry for the images
namespaceConfig: # user can configure labels or annotations that EGS Controller namespaces should have
labels: {}
annotations: {}
kubeTally:
enabled: false # Enable KubeTally in the controller
#### Postgresql Connection Configuration for Kubetally ####
postgresSecretName: kubetally-db-credentials # Secret name in kubeslice-controller namespace for PostgreSQL credentials created by install, all the below values must be specified
# then a secret will be created with specified name.
# alternatively you can make all below values empty and provide a pre-created secret name with below connection details format
postgresAddr: "kt-postgresql.kt-postgresql.svc.cluster.local" # Change this Address to your postgresql endpoint
postgresPort: 5432 # Change this Port for the PostgreSQL service to your values
postgresUser: "postgres" # Change this PostgreSQL username to your values
postgresPassword: "postgres" # Change this PostgreSQL password to your value
postgresDB: "postgres" # Change this PostgreSQL database name to your value
postgresSslmode: disable # Change this SSL mode for PostgreSQL connection to your value
prometheusUrl: http://prometheus-kube-prometheus-prometheus.egs-monitoring.svc.cluster.local:9090 # Prometheus URL for monitoring
kubeslice:
controller:
endpoint: "" # Endpoint of the controller API server; auto-fetched if left empty
#### Helm Flags and Verification Settings ####
helm_flags: "--wait --timeout 5m --debug" # Additional Helm flags for the installation
verify_install: false # Verify the installation of the controller
verify_install_timeout: 30 # Timeout for the controller installation verification (in seconds)
skip_on_verify_fail: true # If verification fails, do not skip the step
#### Troubleshooting Settings ####
enable_troubleshoot: false # Enable troubleshooting mode for additional logs and checks -
(Optional) Configure PostgreSQL to use the KubeTally (Cost Management) feature. The PostgreSQL connection details required by the controller are stored in a Kubernetes Secret in the
kubeslice-controllernamespace. You can configure the secret in one of the following ways:-
To use your own Kubernetes Secret, enter only the secret name in the configuration file and leave other fields blank. Confirm the secret exists in the
kubeslice-controllernamespace and uses the required key-value format.postgresSecretName: kubetally-db-credentials # Existing secret in kubeslice-controller namespace
postgresAddr: ""
postgresPort: ""
postgresUser: ""
postgresPassword: ""
postgresDB: ""
postgresSslmode: "" -
To automatically create a secret, provide all connection details and the secret name. The installer will then create a Kubernetes Secret in the
kubeslice-controllernamespace.postgresSecretName: kubetally-db-credentials # Secret to be created in kubeslice-controller namespace
postgresAddr: "kt-postgresql.kt-postgresql.svc.cluster.local" # PostgreSQL service endpoint
postgresPort: 5432 # PostgreSQL service port (default 5432)
postgresUser: "postgres" # PostgreSQL username
postgresPassword: "postgres" # PostgreSQL password
postgresDB: "postgres" # PostgreSQL database name
postgresSslmode: disable # SSL mode for PostgreSQL connection (for example, disable or require)
-
You can add the kubeslice.io/managed-by-egs=false label to GPU nodes.
This label excludes or filters the associated GPU nodes from the EGS inventory.
Required Inline Configuration for Multi-Cluster Deployments
In multi-cluster deployments, you must configure the global_auto_fetch_endpoint parameter in the egs-installer-config.yaml file.
This configuration is essential for proper monitoring and dashboard URL management across multiple clusters.
In single-cluster deployments, this step is not required, as the controller and worker are in the same cluster.
In multi-cluster setups, the controller and worker clusters may be in different namespaces or even different clusters.
To ensure that the controller can access the monitoring endpoints of the worker clusters, you must set
the global_auto_fetch_endpoint parameter appropriately. Ensure that the Grafana and Prometheus services
are accessible from the controller cluster.
In a multi-cluster deployment, the controller cluster must be able to reach the Prometheus endpoint running on the worker clusters.
If the Prometheus endpoints are not configured, you may experience issues with the dashboards (for example, missing or incomplete metric displays).
For multi-cluster setups, follow these steps to update the inline values in your egs-installer-config.yaml file:
-
Set the
global_auto_fetch_endpointparameter to true.- This parameter enables the automatic fetching of monitoring endpoints from the worker clusters.
- If you set this parameter to true, you must ensure that the worker clusters are properly configured to expose their monitoring endpoints.
-
By default,
global_auto_fetch_endpointis set tofalse. If you set theglobal_auto_fetch_endpointtotrue, ensure the following configurations:- Worker Cluster Service Details: Provide the service details for each worker cluster to fetch the correct monitoring endpoints.
- Multiple Worker Clusters: Ensure the service endpoints (for example, Grafana and Prometheus) are accessible from the controller cluster.
Update the
egs-installer-config.yamlfile with the following inline values:# Global monitoring endpoint settings
global_auto_fetch_endpoint: true # Enable automatic fetching of monitoring endpoints globally
global_grafana_namespace: egs-monitoring # Namespace where Grafana is globally deployed
global_grafana_service_type: ClusterIP # Service type for Grafana (accessible only within the cluster)
global_grafana_service_name: prometheus-grafana # Service name for accessing Grafana globally
global_prometheus_namespace: egs-monitoring # Namespace where Prometheus is globally deployed
global_prometheus_service_name: prometheus-kube-prometheus-prometheus # Service name for accessing Prometheus globally
global_prometheus_service_type: ClusterIP # Service type for Prometheus (accessible only within the cluster) -
If you set
global_auto_fetch_endpointtotrue, the script will automatically fetch the Grafana and Prometheus endpoints from the worker clusters.noteIf you set
global_auto_fetch_endpointtofalse, you must manually specify the Grafana and Prometheus endpoints in theinline_valuesobject of youregs-installer-config.yamlfile.-
Use the following command to get the Prometheus and Grafana LoadBalancer External IP:
kubectl get svc prometheus-grafana -n monitoring
kubectl get svc prometheus -n monitoringExample Output
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
prometheus-grafana LoadBalancer 10.96.0.1 <grafana-lb> 80:31380/TCP 5d
prometheus-kube-prometheus LoadBalancer 10.96.0.2 <prometheus-lb> 9090:31381/TCP 5d -
Update the Prometheus and Grafana LoadBalancer IPs or NodePorts in the
inline_valuessection of youregs-installer-config.yamlfile:inline_values: # Inline Helm values for the worker chart
kubesliceNetworking:
enabled: false # Disable Kubeslice networking for this worker
egs:
prometheusEndpoint: "http://<prometheus-lb>" # Prometheus endpoint
grafanaDashboardBaseUrl: "http://<grafana-lb>/d/Oxed_c6Wz" # Replace <grafana-lb> with the actual External IP
metrics:
insecure: true # Allow insecure connections for metrics
-
Install EGS
- The installation script creates a default project workspace and registers a worker cluster.
- To register an additional worker cluster, use the Admin Portal. For more information, see Register Worker Clusters.
Use the following command to install EGS:
./egs-installer.sh --input-yaml egs-installer-config.yaml
Register a Worker Cluster
If you have already installed EGS and want to register an additional worker cluster, you can update the egs-installer-config.yaml file.
The installation script allows you to register multiple worker clusters at the same time.
To register worker clusters:
- Add worker cluster configuration under:
kubeslice_worker_egsarraycluster_registrationarray
- Repeat the configuration for each worker cluster you want to register.
Example Configuration for Registering a Worker Cluster
To update the configuration file:
-
Add a new worker configuration to the
kubeslice_worker_egsarray in your configuration file:kubeslice_worker_egs:
- name: "worker-1" # Existing worker
# ... existing configuration ...
- name: "worker-2" # New worker
use_global_kubeconfig: true # Use global kubeconfig for this worker
kubeconfig: "" # Path to the kubeconfig file specific to the worker, if empty, uses the global kubeconfig
kubecontext: "" # Kubecontext specific to the worker; if empty, uses the global context
skip_installation: false # Do not skip the installation of the worker
specific_use_local_charts: true # Override to use local charts for this worker
namespace: "kubeslice-system" # Kubernetes namespace for this worker
release: "egs-worker-2" # Helm release name for the worker (must be unique)
chart: "kubeslice-worker-egs" # Helm chart name for the worker
inline_values: # Inline Helm values for the worker chart
global:
imageRegistry: docker.io/aveshasystems # Docker registry for worker images
egs:
prometheusEndpoint: "http://prometheus-kube-prometheus-prometheus.egs-monitoring.svc.cluster.local:9090" # Prometheus endpoint
grafanaDashboardBaseUrl: "http://<grafana-lb>/d/Oxed_c6Wz" # Grafana dashboard base URL
egsAgent:
secretName: egs-agent-access
agentSecret:
endpoint: ""
key: ""
metrics:
insecure: true # Allow insecure connections for metrics
kserve:
enabled: true # Enable KServe for the worker
kserve: # KServe chart options
controller:
gateway:
domain: kubeslice.com
ingressGateway:
className: "nginx" # Ingress class name for the KServe gateway
helm_flags: "--wait --timeout 5m --debug" # Additional Helm flags for the worker installation
verify_install: true # Verify the installation of the worker
verify_install_timeout: 60 # Timeout for the worker installation verification (in seconds)
skip_on_verify_fail: false # Do not skip if worker verification fails
enable_troubleshoot: false # Enable troubleshooting mode for additional logs and checks -
Add a worker cluster registration configuration in the
cluster_registrationarray in your configuration file:cluster_registration:
- cluster_name: "worker-1" # Existing cluster
project_name: "avesha" # Name of the project to associate with the cluster
telemetry:
enabled: true # Enable telemetry for this cluster
endpoint: "http://prometheus-kube-prometheus-prometheus.egs-monitoring.svc.cluster.local:9090" # Telemetry endpoint
telemetryProvider: "prometheus" # Telemetry provider (Prometheus in this case)
geoLocation:
cloudProvider: "" # Cloud provider for this cluster (e.g., GCP)
cloudRegion: "" # Cloud region for this cluster (e.g., us-central1)
- cluster_name: "worker-2" # New cluster
project_name: "avesha" # Name of the project to associate with the cluster
telemetry:
enabled: true # Enable telemetry for this cluster
endpoint: "http://prometheus-kube-prometheus-prometheus.egs-monitoring.svc.cluster.local:9090" # Telemetry endpoint
telemetryProvider: "prometheus" # Telemetry provider (Prometheus in this case)
geoLocation:
cloudProvider: "" # Cloud provider for this cluster (e.g., GCP)
cloudRegion: "" # Cloud region for this cluster (e.g., us-central1)
Run the Installation Script
After adding the new worker configuration, run the installation script to register an additional worker cluster:
./egs-installer.sh --input-yaml egs-installer-config.yaml
Access the Admin Portal
After the successful installation, the script displays the LoadBalancer external IP address and the admin access token to log in to the Admin Portal.
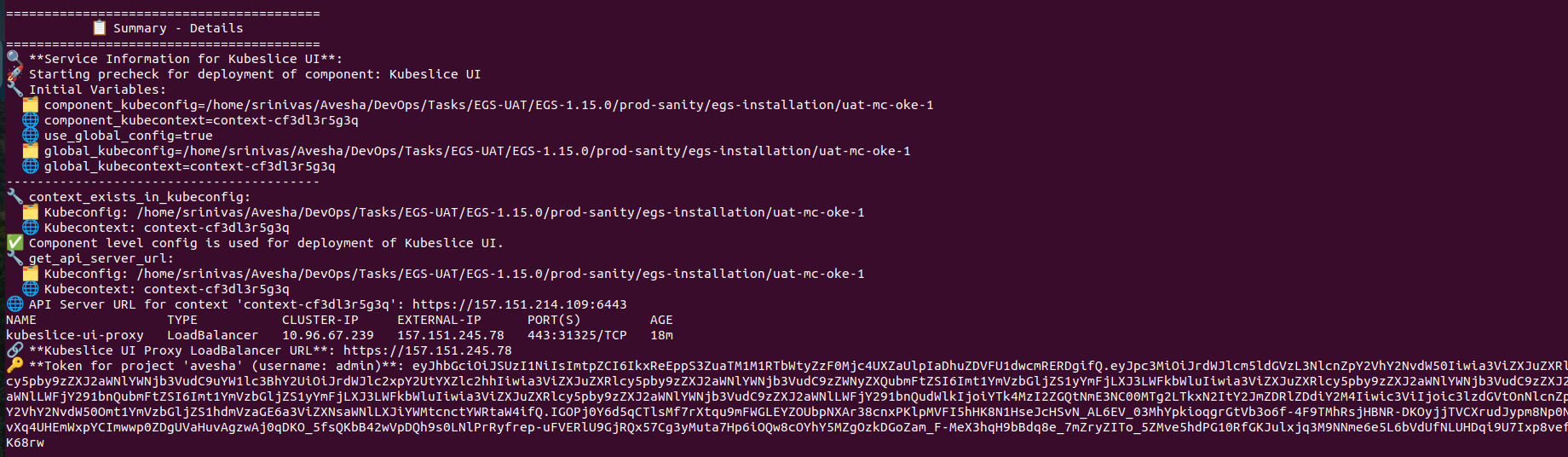
Make a note of the LoadBalancer external IP address and the admin access token required to log in to the Admin Portal. The KubeSlice UI Proxy LoadBalancer URL value is your Admin Portal URL and The token for project avesha (username: admin) is your login token.
Use the URL and the admin access token, from the previous step to log in to the Admin Portal.
Retrieve Admin Credentials Using kubectl
If you missed the LoadBalancer external IP address or the admin access token displayed after installation, you can retrieve them
using kubectl commands.
Perform the following steps to retrieve the admin access token and the Admin Portal URL:
-
Use the following command to retrieve the admin access token:
kubectl get secret kubeslice-rbac-rw-admin -o jsonpath="{.data.token}" -n kubeslice-avesha | base64 --decodeExample Output:
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6IjE2YjY0YzYxY2E3Y2Y0Y2E4YjY0YzYxY2E3Y2Y0Y2E4YjYiLCJ0eXAiOiJKV1QifQ.eyJpc3MiOiJrdWJlcm5ldGVzL3NlcnZpY2UtYWNjb3VudCIsImt1YmVybmV0ZXM6c2VydmljZS1hY2NvdW50Om5hbWUiOiJrdWJlc2xpY2UtcmJhYy1ydy1hZG1pbiIsImt1YmVybmV0ZXM6c2VydmljZS1hY2NvdW50OnVpZCI6Ijg3ZjhiZjBiLTU3ZTAtMTFlYS1iNmJlLTRmNzlhZTIyMWI4NyIsImt1YmVybmV0ZXM6c2VydmljZS1hY2NvdW50OnNlcnZpY2UtYWNjb3VudC51aWQiOiI4N2Y4YmYwYi01N2UwLTExZWEtYjZiZS00Zjc5YWUyMjFiODciLCJzdWIiOiJzeXN0ZW06c2VydmljZWFjY291bnQ6a3ViZXNsaWNlLXJiYWMtcnctYWRtaW4ifQ.MEYCIQDfXoX8v7b8k7c3
4mJpXHh3Zk5lYzVtY2Z0eXlLQAIhAJi0r5c1v6vUu8mJxYv1j6Kz3p7G9y4nU5r8yX9fX6c -
Use the following command to access the Load Balancer IP:
Example
kubectl get svc -n kubeslice-controller | grep kubeslice-ui-proxyExample Output
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubeslice-ui-proxy LoadBalancer 10.96.2.238 172.18.255.201 443:31751/TCP 24h
Note down the LoadBalancer external IP of the kubeslice-ui-proxy pod. In the above example, 172.18.255.201 is
the external IP. The EGS Portal URL will be https://<ui-proxy-ip>.
Upload Custom Pricing for Cloud Resources
To upload custom pricing for cloud resources, you can use the custom-pricing-upload.sh script provided in the EGS installation repository.
This script allows you to upload custom pricing data for various cloud resources, which can be used for cost estimation and budgeting.
Ensure you have installed curl to upload the CSV file.
To upload custom pricing data:
-
Navigate to the cloned
egs-installationrepository and change the file permission using the following command:chmod +x custom-pricing-upload.sh -
Use the
customer-pricing-data.yamlfile to specify the custom pricing data. The file should contain the following structure:kubernetes:
kubeconfig: "" #absolute path of kubeconfig
kubecontext: "" #kubecontext name
namespace: "kubeslice-controller"
service: "kubetally-pricing-service"
#we can add as many cloud providers and instance types as needed
cloud_providers:
- name: "gcp"
instances:
- region: "us-east1"
component: "Compute Instance"
instance_type: "a2-highgpu-2g"
vcpu: 1
price: 20
gpu: 1
- region: "us-east1"
component: "Compute Instance"
instance_type: "e2-standard-8"
vcpu: 1
price: 5
gpu: 0 -
Run the script to upload the custom pricing data:
./custom-pricing-upload.sh
This script automates the process of loading custom cloud pricing data into the pricing API running inside a Kubernetes cluster.
Script Workflow:
-
Reads the cluster connection details (kubeconfig, context) from the YAML input file.
-
Identifies the target service and its exposed port (for example, kubetally-pricing-service:80).
-
Selects a random available local port on the host machine.
-
Establishes a port-forwarding tunnel from the selected local port to the Kubernetes service. Runs in the background to keep the tunnel active during upload.
-
Converts the pricing data from YAML format into CSV format for API ingestion.
-
Uploads the generated CSV file to the pricing API at:
http://localhost:<random_port>/api/v1/prices
Uninstall EGS
The uninstallation script removes all resources associated with EGS, including:
- Workspaces
- GPU Provision Requests (GPRs)
- All custom resources provisioned by EGS
Before running the uninstallation script, ensure that you have backed up any important data or configurations. The script will remove all EGS-related resources, and this action cannot be undone.
Use the following command to uninstall EGS:
./egs-uninstall.sh --input-yaml egs-installer-config.yaml
Troubleshooting
-
Missing Binaries
Ensure all required binaries are installed and available in your system’s PATH.
-
Cluster Access Issues
Verify that your
kubeconfigfiles are correctly configured so the script can access the clusters defined in the YAML configuration. -
Timeout Issues
If a component fails to install within the specified timeout, increase the
verify_install_timeoutvalue in the YAML file.